Unveiling the Nuances of AI Detection: A Comprehensive Guide and Latest Research Findings
In the AI Detection revolution, the ability to distinguish between human-induced and AI-induced effects has become increasingly important in the specialized context of artificial intelligence (AI). -Explores a range of premium options
Important to introduce AI in processed products
As AI technology evolves, so does the power of AI discovery tools. Originally designed for simple pattern recognition, these tools have evolved to use sophisticated recognition systems capable of discriminating the effects of advanced patterns such as GPT-3 and GPT-4.


The emerging role of AI in education, digital marketing, and manufacturing underscores the need for a strong AI identity. These tools play an important role in preserving content integrity and maintaining academic integrity, ensuring that quality and originality are not compromised by the proliferation of AI in content production.
Comparing Free and Paid AI Detection Tools
Each AI detection tool brings its own unique features to the table:
Free Tools:
Suited for individual or small-scale use, these tools provide basic detection capabilities. While user-friendly, they may lack the depth of analysis offered by their premium counterparts.
Paid Tools:
Geared towards businesses and professional settings, paid tools offer advanced detection features and higher accuracy, and often come with additional support and customization options. They prove invaluable for detailed analysis and comprehensive content examination.
While free tools suffice for casual users, businesses and professionals seeking detailed analysis should consider investing in premium tools based on their specific requirements.
Leading AI Detection Tools in 2024
1. Copy Leaks:
A comprehensive suite comprising the award-winning Plagiarism Detector, Codeleaks Source Code Detector, and the new Grammar Checker API. This full-spectrum solution is dedicated to creating original, error-free content.
2. Undetectable AI:
Crafted to outsmart AI content detectors, this tool utilizes cutting-edge algorithms and sophisticated paraphrasing techniques. Ideal for writers, bloggers, researchers, and content creators aiming to generate undetectable, search-engine-optimized material.
3. Scribbr:
Leveraging AI and the ChatGPT Detector, Scribbr confidently identifies texts generated by popular tools like ChatGPT, Bard, and Bing Chat. It offers a convenient free check option.
AI Content Detection: Bard vs. ChatGPT vs. Claude
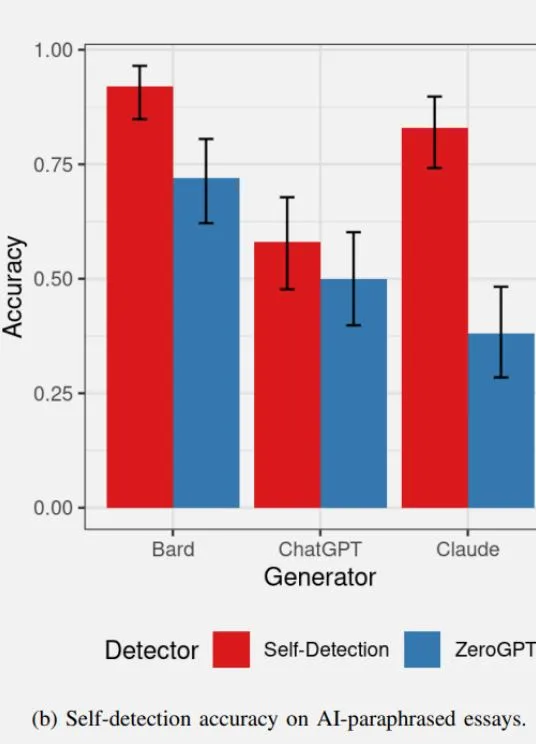
Recent research delves into the self-detection abilities of AI models, shedding light on the distinctive features of Bard, ChatGPT, and Claude. Surprisingly, Claude’s content proved the most challenging to detect, raising intriguing questions about the uniqueness of AI-generated artifacts.

Insights from Research on Self-Detection
Researchers conducted tests on three AI models – ChatGPT-3.5, Bard, and Claude – exploring their self-detection capabilities. The results revealed that each AI model exhibited varying success rates in self-identifying its own content. Claude emerged as an outlier, struggling to detect its own content, indicating a potentially higher quality in output with fewer AI artifacts.
Key Findings and Implications
The study showcased:
–Bard and ChatGPT had a higher accuracy in self-detecting their own original content.
– Claude‘s content was notably harder to detect, suggesting fewer discernible artifacts.
– Self-detection of paraphrased content yielded unexpected results, with Claude outperforming the other models.
The researchers suggested that the uniqueness of AI-generated artifacts contributes to an AI’s success in self-identifying its content, highlighting the complexity of developing a universal detector for all generative AI models.
Conclusion and Future Perspectives
As AI detection tools continue to evolve, understanding their capabilities and limitations becomes paramount. Whether opting for free or premium solutions, users must align their choices with specific needs. The research findings underline the dynamic nature of AI self-detection, with potential implications for the ongoing development of AI content detection tools.